-

 The Occupational Safety Health Administration (OSHA) reports that scaffolding accidents attribute to an estimated 9,000 injuries and 79 fatalities annually. No matter how safe or sturdy a scaffold may look, it can only support a specific weight capacity specified by the manufacturer. Workers must recognize terms associated with capacity limits when working with scaffolds. This course will help you work safely and follow best practices when working on scaffolding.
The Occupational Safety Health Administration (OSHA) reports that scaffolding accidents attribute to an estimated 9,000 injuries and 79 fatalities annually. No matter how safe or sturdy a scaffold may look, it can only support a specific weight capacity specified by the manufacturer. Workers must recognize terms associated with capacity limits when working with scaffolds. This course will help you work safely and follow best practices when working on scaffolding. -

 Operating aerial lifts safely begins with preventive maintenance and conditioning of machinery, and there are a lot of considerations before even turning on the key, but the majority of aerial lift accidents happen because of a lack of training or inattention. The most common hazards involving aerial lifts are falls, tip-overs, ejections, structural failure, and electrocution. Inexperience with equipment is another common factor in aerial lift accidents. At a minimum you need to be familiar with correct lift operation, how to perform inspections, and knowledge of manufacturers’ requirements.
Operating aerial lifts safely begins with preventive maintenance and conditioning of machinery, and there are a lot of considerations before even turning on the key, but the majority of aerial lift accidents happen because of a lack of training or inattention. The most common hazards involving aerial lifts are falls, tip-overs, ejections, structural failure, and electrocution. Inexperience with equipment is another common factor in aerial lift accidents. At a minimum you need to be familiar with correct lift operation, how to perform inspections, and knowledge of manufacturers’ requirements. -

 You don’t need numbers to know that radio communication saves lives. Think of how vital radio communication is to the ship that’s sending out a distress call, or for the airplane experiencing technical issues, or for the first responders to a natural disaster. Or, what about people working in isolation in high-risk work environments, like corrections personnel, or a team of backcountry firefighters? A functional radio communications system can mean the difference between life and death. When time is of the essence and someone needs immediate medical attention, a radio carries the promise of a better outcome, so it is important to understand how they work and what they can and cannot do, and what rules govern the use of these systems.
You don’t need numbers to know that radio communication saves lives. Think of how vital radio communication is to the ship that’s sending out a distress call, or for the airplane experiencing technical issues, or for the first responders to a natural disaster. Or, what about people working in isolation in high-risk work environments, like corrections personnel, or a team of backcountry firefighters? A functional radio communications system can mean the difference between life and death. When time is of the essence and someone needs immediate medical attention, a radio carries the promise of a better outcome, so it is important to understand how they work and what they can and cannot do, and what rules govern the use of these systems. -

 Process safety management increases safety for the workforce. Now, small businesses with limited resources might use other ways to decrease the risks associated with hazardous chemicals in the workplace, but development of a process safety management program is the operating standard. An effective process safety management program requires employers to compile a written process information resource. This information enables workers to identify and understand the hazards posed by processes that involve highly hazardous chemicals.
Process safety management increases safety for the workforce. Now, small businesses with limited resources might use other ways to decrease the risks associated with hazardous chemicals in the workplace, but development of a process safety management program is the operating standard. An effective process safety management program requires employers to compile a written process information resource. This information enables workers to identify and understand the hazards posed by processes that involve highly hazardous chemicals. -
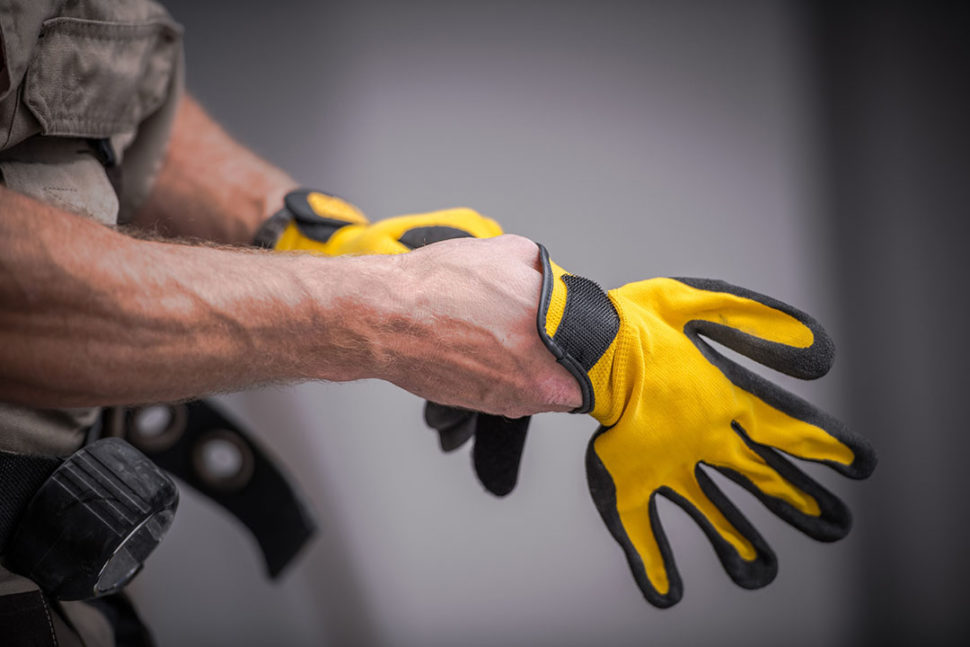
 Can you put a price tag on the use of your hands? Some people don't realize the important of their hands until they aren't able to be used any longer. Hand injuries send a million workers to ERs each year, and hand injuries are the No. 2 leading cause of work-related injury and the most preventable through proper personal protective equipment (PPE).
Can you put a price tag on the use of your hands? Some people don't realize the important of their hands until they aren't able to be used any longer. Hand injuries send a million workers to ERs each year, and hand injuries are the No. 2 leading cause of work-related injury and the most preventable through proper personal protective equipment (PPE). -
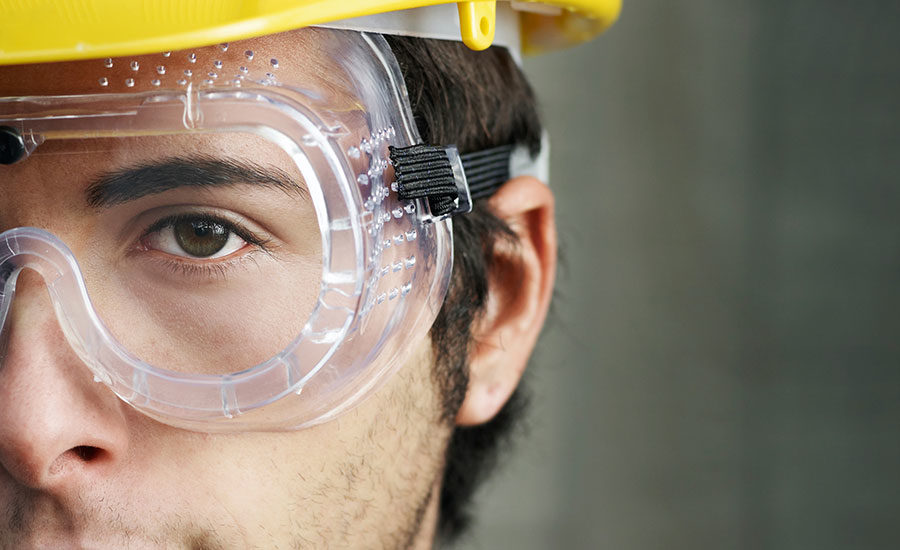
 Approximately 770 workers suffer face injuries on a yearly basis; most don't wear proper personal protective equipment (PPE) for face protection Proper personal protective equipment (PPE) is essential to any work environment for eye and face protection. The goal of this course is to show how to handle face and eye protection properly using personal protective equipment (PPE).
Approximately 770 workers suffer face injuries on a yearly basis; most don't wear proper personal protective equipment (PPE) for face protection Proper personal protective equipment (PPE) is essential to any work environment for eye and face protection. The goal of this course is to show how to handle face and eye protection properly using personal protective equipment (PPE). -
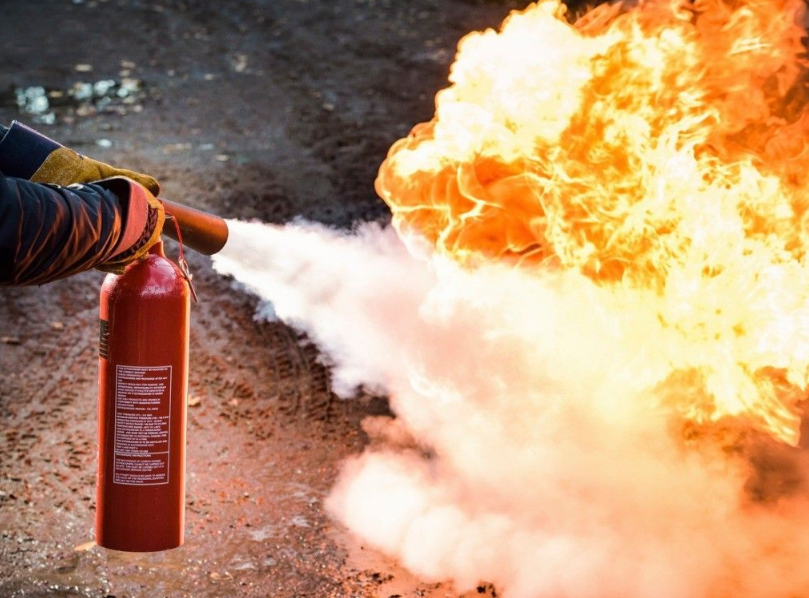
 Fire extinguishers are one of the most reliable ways to put out fires in the workplace. Fire extinguishers are not a requirement, but if employers choose to provide them they must train workers in general fire extinguisher use to comply with OSHA standards. OSHA states that if employers expect workers to use the fire extinguishers themselves, hands-on training must be provided.
Fire extinguishers are one of the most reliable ways to put out fires in the workplace. Fire extinguishers are not a requirement, but if employers choose to provide them they must train workers in general fire extinguisher use to comply with OSHA standards. OSHA states that if employers expect workers to use the fire extinguishers themselves, hands-on training must be provided. -
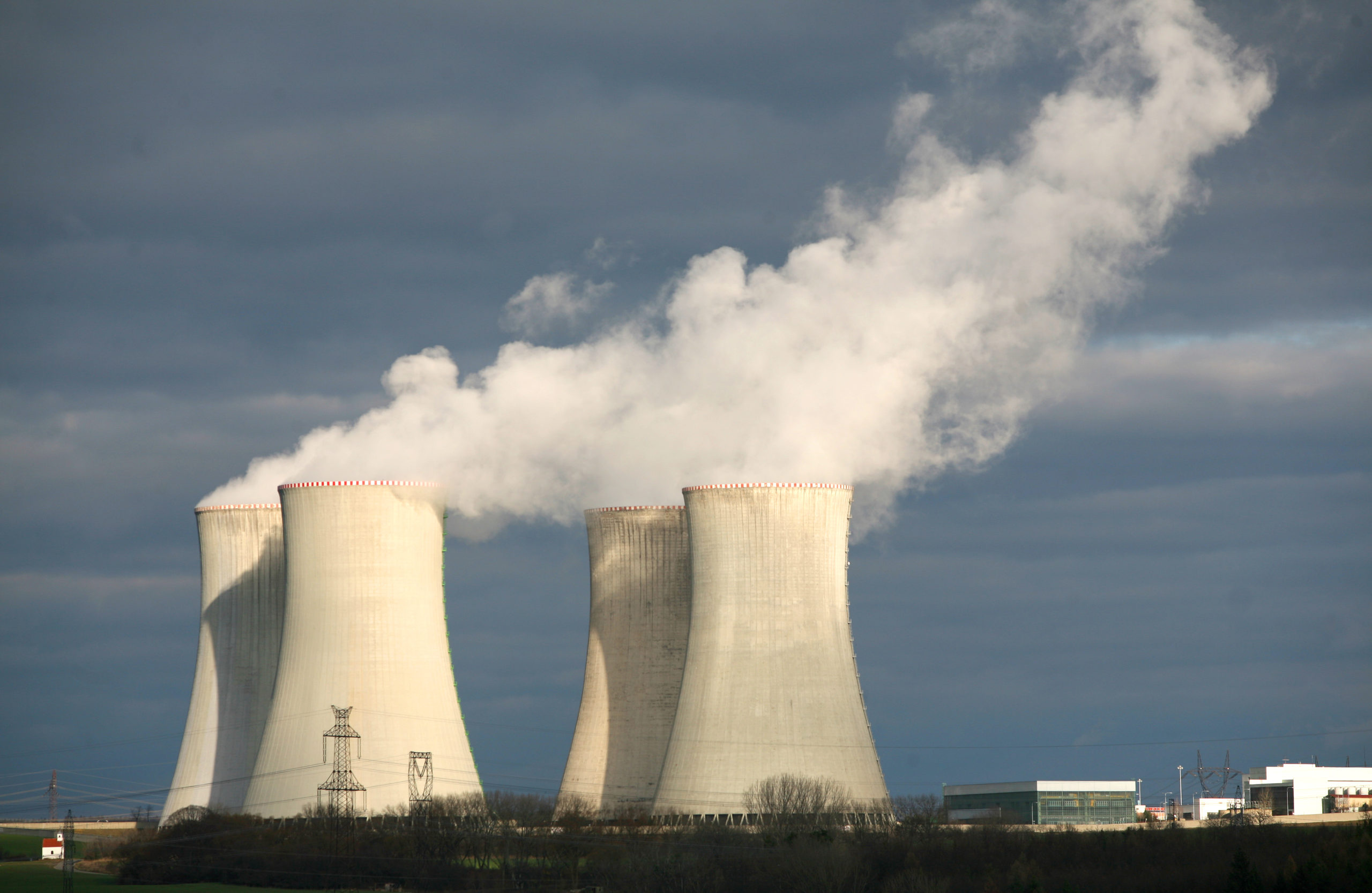
 Nuclear criticality accidents have killed, but these accidents don’t happen often because when they do occur, the results have historically proven disastrous; regulations, training, and procedural safeguards have all intensified in the wake of high-profile, fatal events around the world. Accidental criticality is a hazard unique to facilities where fissionable materials are handled or stored, such as nuclear fuel manufacturing and processing facilities. The Nuclear Regulatory Commission characterizes these events as “uncontrolled nuclear fission chain reactions.” So, that’s what we’re talking about, and unexpected, unplanned nuclear episode that poses risk to human health and wellbeing proportionate to the size of event and proximity of those exposed.
Nuclear criticality accidents have killed, but these accidents don’t happen often because when they do occur, the results have historically proven disastrous; regulations, training, and procedural safeguards have all intensified in the wake of high-profile, fatal events around the world. Accidental criticality is a hazard unique to facilities where fissionable materials are handled or stored, such as nuclear fuel manufacturing and processing facilities. The Nuclear Regulatory Commission characterizes these events as “uncontrolled nuclear fission chain reactions.” So, that’s what we’re talking about, and unexpected, unplanned nuclear episode that poses risk to human health and wellbeing proportionate to the size of event and proximity of those exposed. -
 The purpose of the NFPA standard 70E is to provide a standard for safety-related work practices for the construction, maintenance, operation and demolition of electrical systems in the workplace. This Overview covers awareness-level information for workers who have jobs or assignments that bring them into contact with electrical hazards, such as arc flash and electric shock. Completing this lesson does not designate an employee as an electrically-qualified worker.
The purpose of the NFPA standard 70E is to provide a standard for safety-related work practices for the construction, maintenance, operation and demolition of electrical systems in the workplace. This Overview covers awareness-level information for workers who have jobs or assignments that bring them into contact with electrical hazards, such as arc flash and electric shock. Completing this lesson does not designate an employee as an electrically-qualified worker. -

 To protect you from the serious hazards posed by the unexpected start-up or operation of equipment during repair or maintenance, the Occupational Safety & Health Administration (OSHA) has established a Control of Hazardous Energy standard. It is commonly referred to as the lockout/tagout (LOTO), or energy isolation standard. This standard requires the application of markings and barriers that prevent unauthorized persons from energizing and operating equipment.Energy in any form becomes hazardous when it builds to a certain level or is released inadvertently or unexpectedly. Lockout/tagout refers to specific practices and procedures that safeguard employees from the unexpected startup of machinery and equipment, or the release of hazardous energy, during service or maintenance activities.
To protect you from the serious hazards posed by the unexpected start-up or operation of equipment during repair or maintenance, the Occupational Safety & Health Administration (OSHA) has established a Control of Hazardous Energy standard. It is commonly referred to as the lockout/tagout (LOTO), or energy isolation standard. This standard requires the application of markings and barriers that prevent unauthorized persons from energizing and operating equipment.Energy in any form becomes hazardous when it builds to a certain level or is released inadvertently or unexpectedly. Lockout/tagout refers to specific practices and procedures that safeguard employees from the unexpected startup of machinery and equipment, or the release of hazardous energy, during service or maintenance activities. -
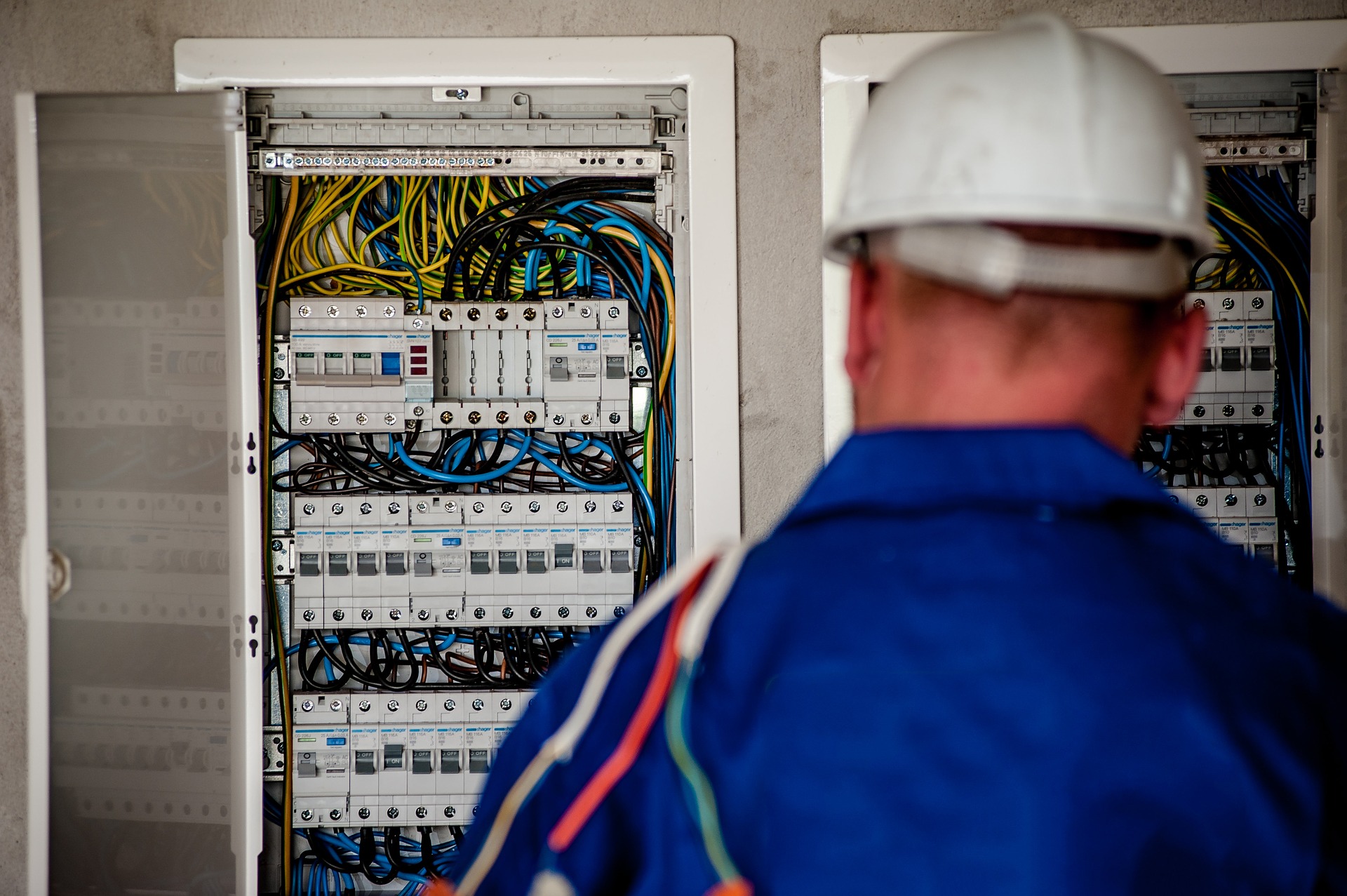 The purpose of the NFPA standard 70E is to provide a standard for safety-related work practices for the construction, maintenance, operation and demolition of electrical systems in the workplace. This Overview covers awareness-level information for workers who have jobs or assignments that bring them into contact with electrical hazards, such as arc flash and electric shock. Completing this lesson does not designate an employee as an electrically-qualified worker.
The purpose of the NFPA standard 70E is to provide a standard for safety-related work practices for the construction, maintenance, operation and demolition of electrical systems in the workplace. This Overview covers awareness-level information for workers who have jobs or assignments that bring them into contact with electrical hazards, such as arc flash and electric shock. Completing this lesson does not designate an employee as an electrically-qualified worker. -
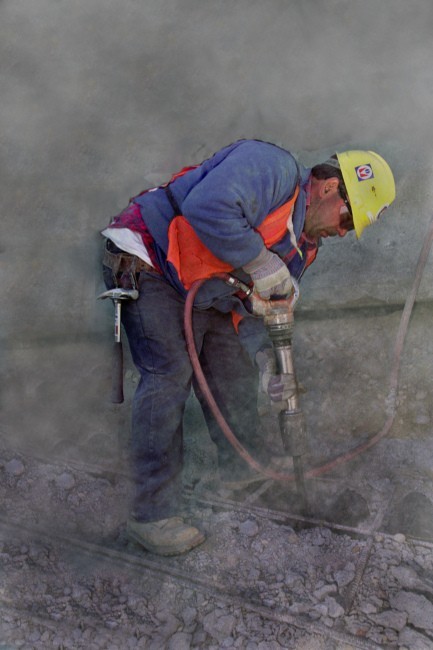
 The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has issued a final rule to curb lung cancer, silicosis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and kidney disease in America's workers by limiting their exposure to respirable crystalline silica. The rule is comprised of two standards, one for Construction and one for General Industry and Maritime. This lesson is designed to improve the safety of workers in environments where silica exposure hazards exist by increasing employee awareness of this hazard and by demonstrating how the hazard can be recognized and addressed in the workplace.
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has issued a final rule to curb lung cancer, silicosis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and kidney disease in America's workers by limiting their exposure to respirable crystalline silica. The rule is comprised of two standards, one for Construction and one for General Industry and Maritime. This lesson is designed to improve the safety of workers in environments where silica exposure hazards exist by increasing employee awareness of this hazard and by demonstrating how the hazard can be recognized and addressed in the workplace. -

 This lesson describes the importance of safety in the workplace and the employee’s role in maintaining a safe workplace. According to the National Federation of Independent Businesses defines ideal safety accountability as ideal accountability along with companies that strive for optimal safety performance display the highest level of organizational safety accountability.
This lesson describes the importance of safety in the workplace and the employee’s role in maintaining a safe workplace. According to the National Federation of Independent Businesses defines ideal safety accountability as ideal accountability along with companies that strive for optimal safety performance display the highest level of organizational safety accountability. -
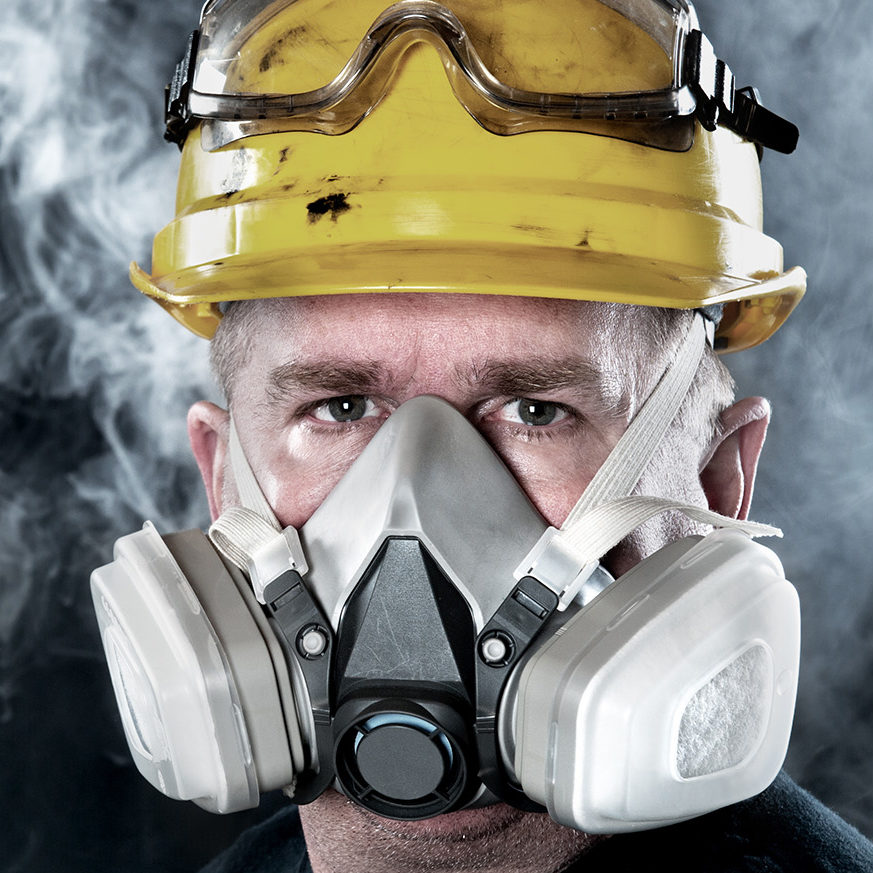
 In this course you’ll learn about the chemistry of Hydrogen Sulfide and how it is formed, the properties and characteristics of the gas, where Hydrogen Sulfide is likely to be located in your workplace, the potential health hazards of short term and long term H2S exposure, how to work safely with Hydrogen Sulfide and emergency response steps to take should you or a co-worker be exposed to this gas.
In this course you’ll learn about the chemistry of Hydrogen Sulfide and how it is formed, the properties and characteristics of the gas, where Hydrogen Sulfide is likely to be located in your workplace, the potential health hazards of short term and long term H2S exposure, how to work safely with Hydrogen Sulfide and emergency response steps to take should you or a co-worker be exposed to this gas. -
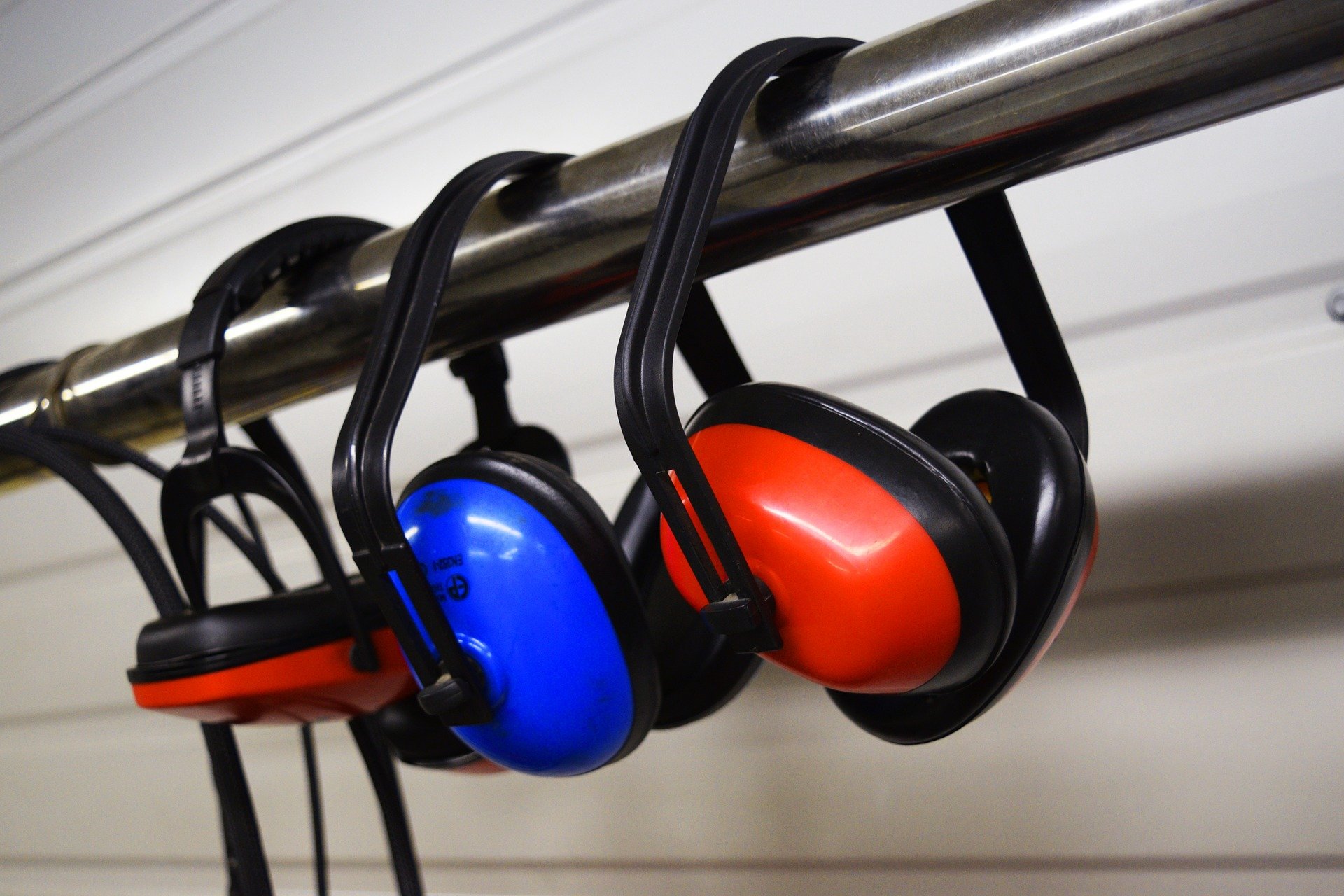
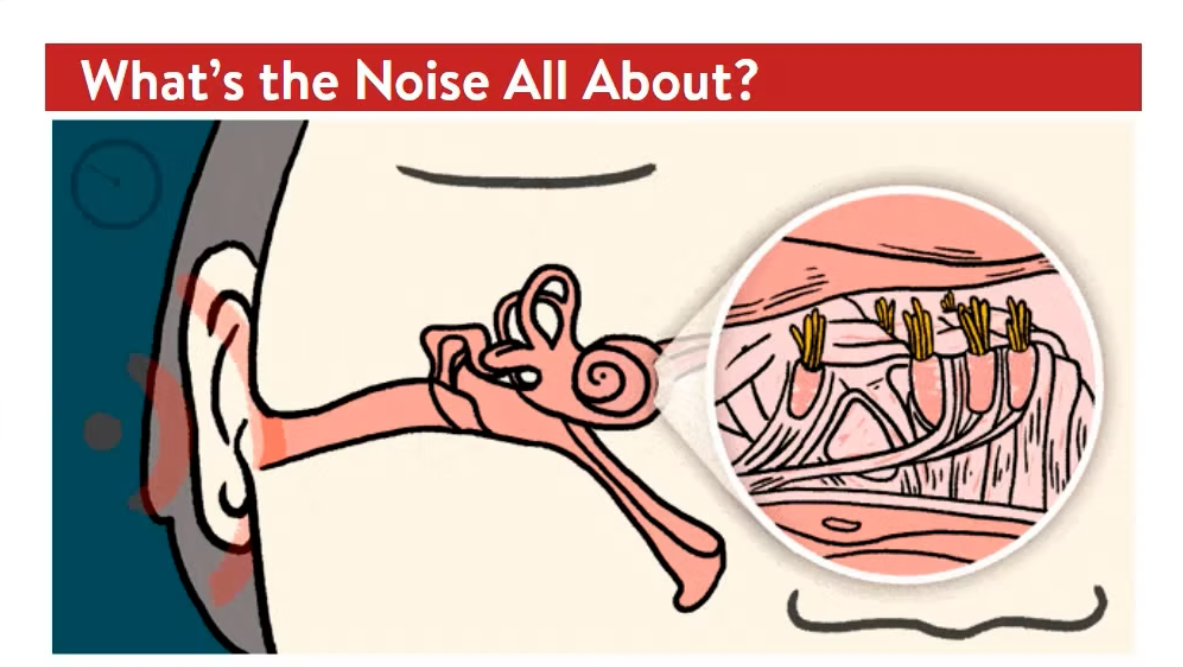
 In this course you will learn how to identify how noise impacts hearing and the factors that determine the extent of hearing loss, identify noise exposure levels that require hearing protection according to Part VII of Canadian Regulations, identify how the types of hearing protectors are selected for a job, and their advantages and disadvantages for controlling noise exposure, identify correct use, care, and maintenance practices for hearing protectors and identify the requirements of a Hearing Conservation Program.
In this course you will learn how to identify how noise impacts hearing and the factors that determine the extent of hearing loss, identify noise exposure levels that require hearing protection according to Part VII of Canadian Regulations, identify how the types of hearing protectors are selected for a job, and their advantages and disadvantages for controlling noise exposure, identify correct use, care, and maintenance practices for hearing protectors and identify the requirements of a Hearing Conservation Program.