-
 Nuclear criticality accidents have killed, but these accidents don’t happen often because when they do occur, the results have historically proven disastrous; regulations, training, and procedural safeguards have all intensified in the wake of high-profile, fatal events around the world. Accidental criticality is a hazard unique to facilities where fissionable materials are handled or stored, such as nuclear fuel manufacturing and processing facilities. The Nuclear Regulatory Commission characterizes these events as “uncontrolled nuclear fission chain reactions.” So, that’s what we’re talking about, and unexpected, unplanned nuclear episode that poses risk to human health and wellbeing proportionate to the size of event and proximity of those exposed.
Nuclear criticality accidents have killed, but these accidents don’t happen often because when they do occur, the results have historically proven disastrous; regulations, training, and procedural safeguards have all intensified in the wake of high-profile, fatal events around the world. Accidental criticality is a hazard unique to facilities where fissionable materials are handled or stored, such as nuclear fuel manufacturing and processing facilities. The Nuclear Regulatory Commission characterizes these events as “uncontrolled nuclear fission chain reactions.” So, that’s what we’re talking about, and unexpected, unplanned nuclear episode that poses risk to human health and wellbeing proportionate to the size of event and proximity of those exposed. -
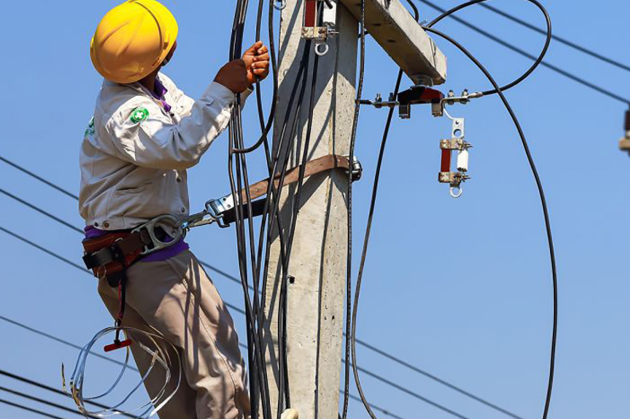
 The purpose of the NFPA standard 70E is to provide a standard for safety-related work practices for the construction, maintenance, operation and demolition of electrical systems in the workplace. This Overview covers awareness-level information for workers who have jobs or assignments that bring them into contact with electrical hazards, such as arc flash and electric shock. Completing this lesson does not designate an employee as an electrically-qualified worker.
The purpose of the NFPA standard 70E is to provide a standard for safety-related work practices for the construction, maintenance, operation and demolition of electrical systems in the workplace. This Overview covers awareness-level information for workers who have jobs or assignments that bring them into contact with electrical hazards, such as arc flash and electric shock. Completing this lesson does not designate an employee as an electrically-qualified worker. -

 To protect you from the serious hazards posed by the unexpected start-up or operation of equipment during repair or maintenance, the Occupational Safety & Health Administration (OSHA) has established a Control of Hazardous Energy standard. It is commonly referred to as the lockout/tagout (LOTO), or energy isolation standard. This standard requires the application of markings and barriers that prevent unauthorized persons from energizing and operating equipment.Energy in any form becomes hazardous when it builds to a certain level or is released inadvertently or unexpectedly. Lockout/tagout refers to specific practices and procedures that safeguard employees from the unexpected startup of machinery and equipment, or the release of hazardous energy, during service or maintenance activities.
To protect you from the serious hazards posed by the unexpected start-up or operation of equipment during repair or maintenance, the Occupational Safety & Health Administration (OSHA) has established a Control of Hazardous Energy standard. It is commonly referred to as the lockout/tagout (LOTO), or energy isolation standard. This standard requires the application of markings and barriers that prevent unauthorized persons from energizing and operating equipment.Energy in any form becomes hazardous when it builds to a certain level or is released inadvertently or unexpectedly. Lockout/tagout refers to specific practices and procedures that safeguard employees from the unexpected startup of machinery and equipment, or the release of hazardous energy, during service or maintenance activities. -
 The purpose of the NFPA standard 70E is to provide a standard for safety-related work practices for the construction, maintenance, operation and demolition of electrical systems in the workplace. This Overview covers awareness-level information for workers who have jobs or assignments that bring them into contact with electrical hazards, such as arc flash and electric shock. Completing this lesson does not designate an employee as an electrically-qualified worker.
The purpose of the NFPA standard 70E is to provide a standard for safety-related work practices for the construction, maintenance, operation and demolition of electrical systems in the workplace. This Overview covers awareness-level information for workers who have jobs or assignments that bring them into contact with electrical hazards, such as arc flash and electric shock. Completing this lesson does not designate an employee as an electrically-qualified worker. -
 The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has issued a final rule to curb lung cancer, silicosis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and kidney disease in America's workers by limiting their exposure to respirable crystalline silica. The rule is comprised of two standards, one for Construction and one for General Industry and Maritime. This lesson is designed to improve the safety of workers in environments where silica exposure hazards exist by increasing employee awareness of this hazard and by demonstrating how the hazard can be recognized and addressed in the workplace.
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has issued a final rule to curb lung cancer, silicosis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and kidney disease in America's workers by limiting their exposure to respirable crystalline silica. The rule is comprised of two standards, one for Construction and one for General Industry and Maritime. This lesson is designed to improve the safety of workers in environments where silica exposure hazards exist by increasing employee awareness of this hazard and by demonstrating how the hazard can be recognized and addressed in the workplace. -

 This lesson describes the importance of safety in the workplace and the employee’s role in maintaining a safe workplace. According to the National Federation of Independent Businesses defines ideal safety accountability as ideal accountability along with companies that strive for optimal safety performance display the highest level of organizational safety accountability.
This lesson describes the importance of safety in the workplace and the employee’s role in maintaining a safe workplace. According to the National Federation of Independent Businesses defines ideal safety accountability as ideal accountability along with companies that strive for optimal safety performance display the highest level of organizational safety accountability. -
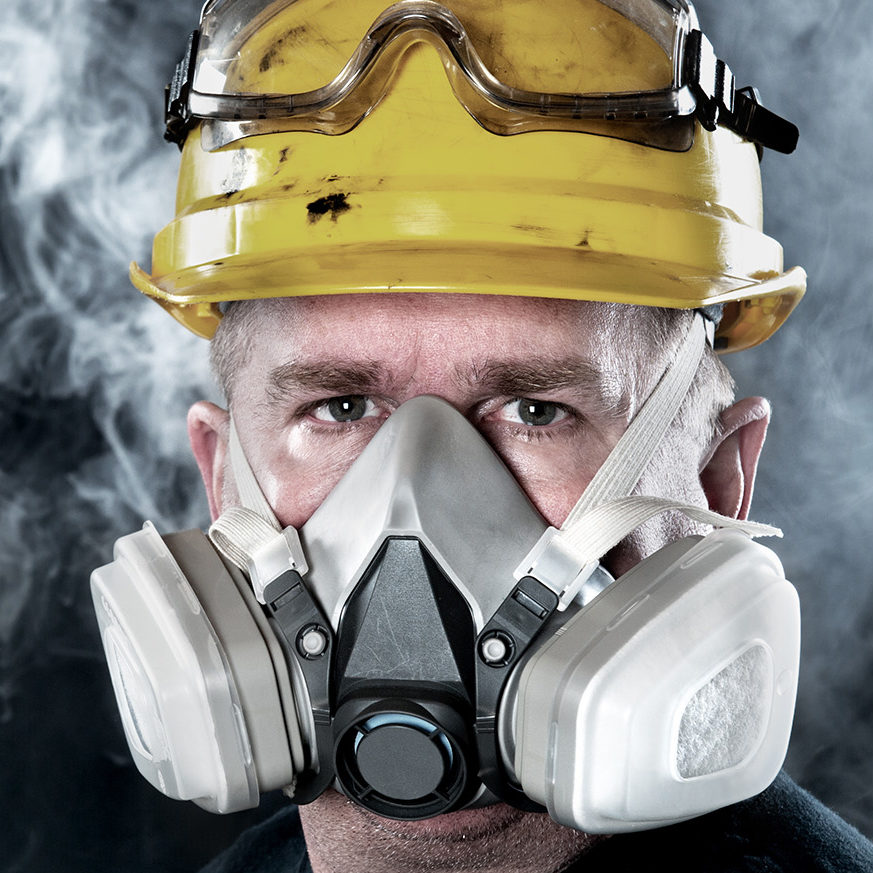
 In this course you’ll learn about the chemistry of Hydrogen Sulfide and how it is formed, the properties and characteristics of the gas, where Hydrogen Sulfide is likely to be located in your workplace, the potential health hazards of short term and long term H2S exposure, how to work safely with Hydrogen Sulfide and emergency response steps to take should you or a co-worker be exposed to this gas.
In this course you’ll learn about the chemistry of Hydrogen Sulfide and how it is formed, the properties and characteristics of the gas, where Hydrogen Sulfide is likely to be located in your workplace, the potential health hazards of short term and long term H2S exposure, how to work safely with Hydrogen Sulfide and emergency response steps to take should you or a co-worker be exposed to this gas. -
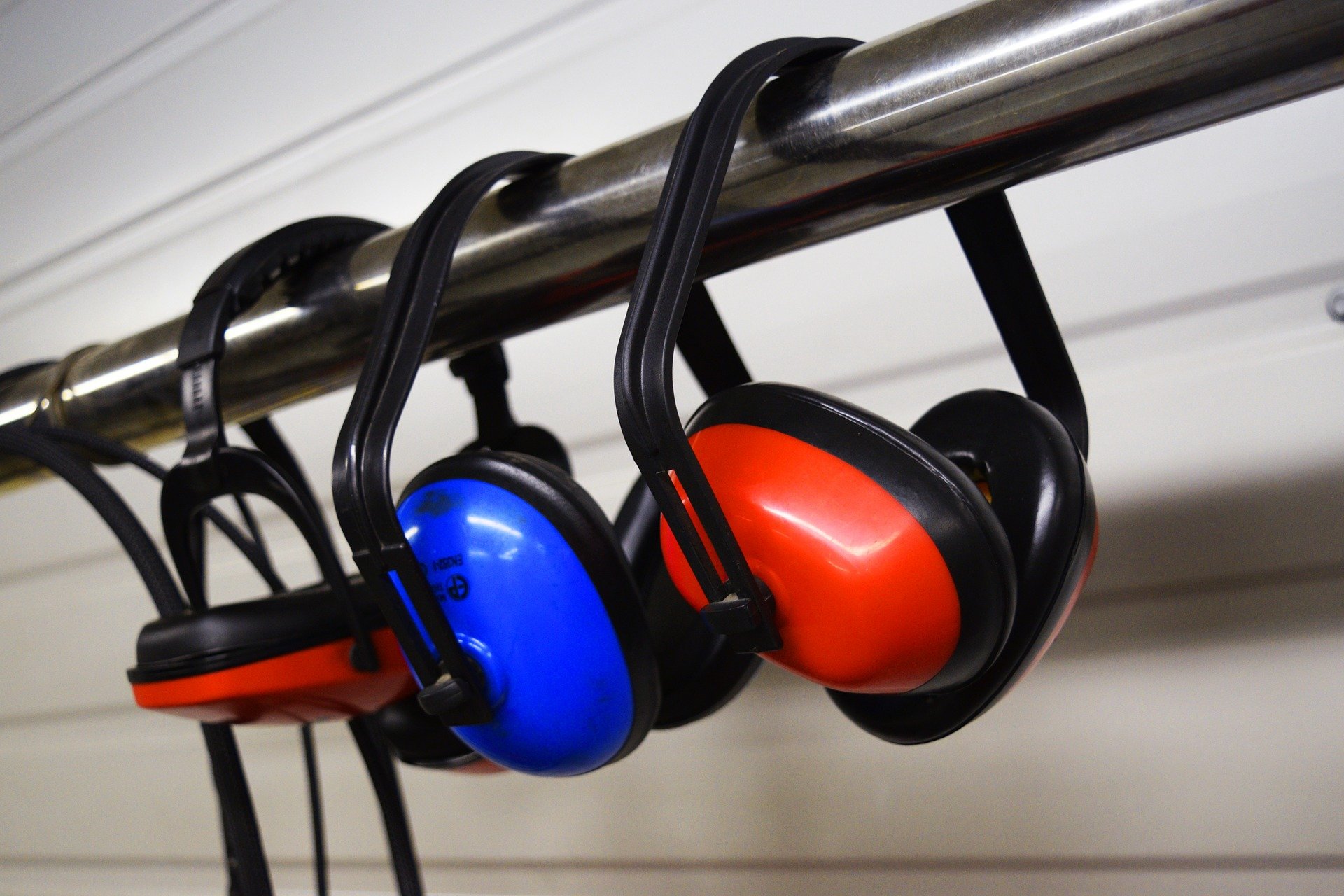
 In this course you will learn how to identify how noise impacts hearing and the factors that determine the extent of hearing loss, identify noise exposure levels that require hearing protection according to Part VII of Canadian Regulations, identify how the types of hearing protectors are selected for a job, and their advantages and disadvantages for controlling noise exposure, identify correct use, care, and maintenance practices for hearing protectors and identify the requirements of a Hearing Conservation Program.
In this course you will learn how to identify how noise impacts hearing and the factors that determine the extent of hearing loss, identify noise exposure levels that require hearing protection according to Part VII of Canadian Regulations, identify how the types of hearing protectors are selected for a job, and their advantages and disadvantages for controlling noise exposure, identify correct use, care, and maintenance practices for hearing protectors and identify the requirements of a Hearing Conservation Program. -

 Emergency planning is critical for operations that handle or produce significant quantities of hazardous materials. Because of the danger to employees working at these facilities and to the general public presented by the harmful release of hazardous materials, likes noxious, combustible gases and waste, people have a right to know about the potential for danger involved in related operations.
Emergency planning is critical for operations that handle or produce significant quantities of hazardous materials. Because of the danger to employees working at these facilities and to the general public presented by the harmful release of hazardous materials, likes noxious, combustible gases and waste, people have a right to know about the potential for danger involved in related operations. -
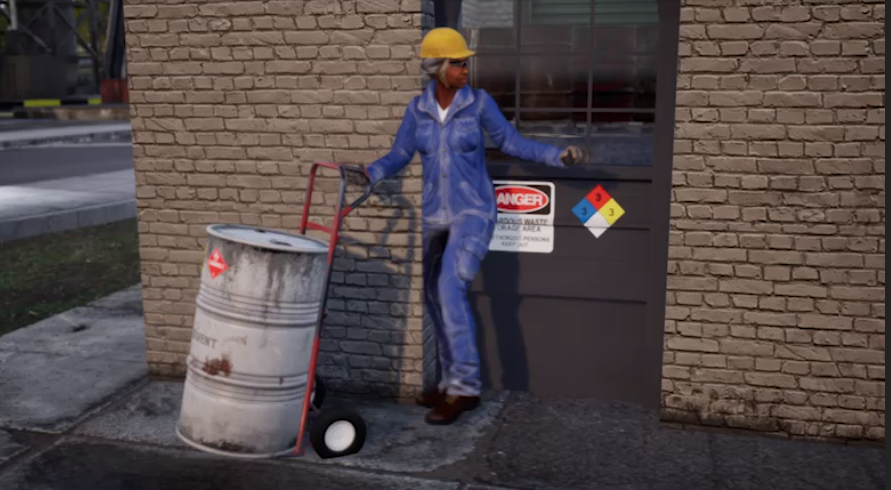
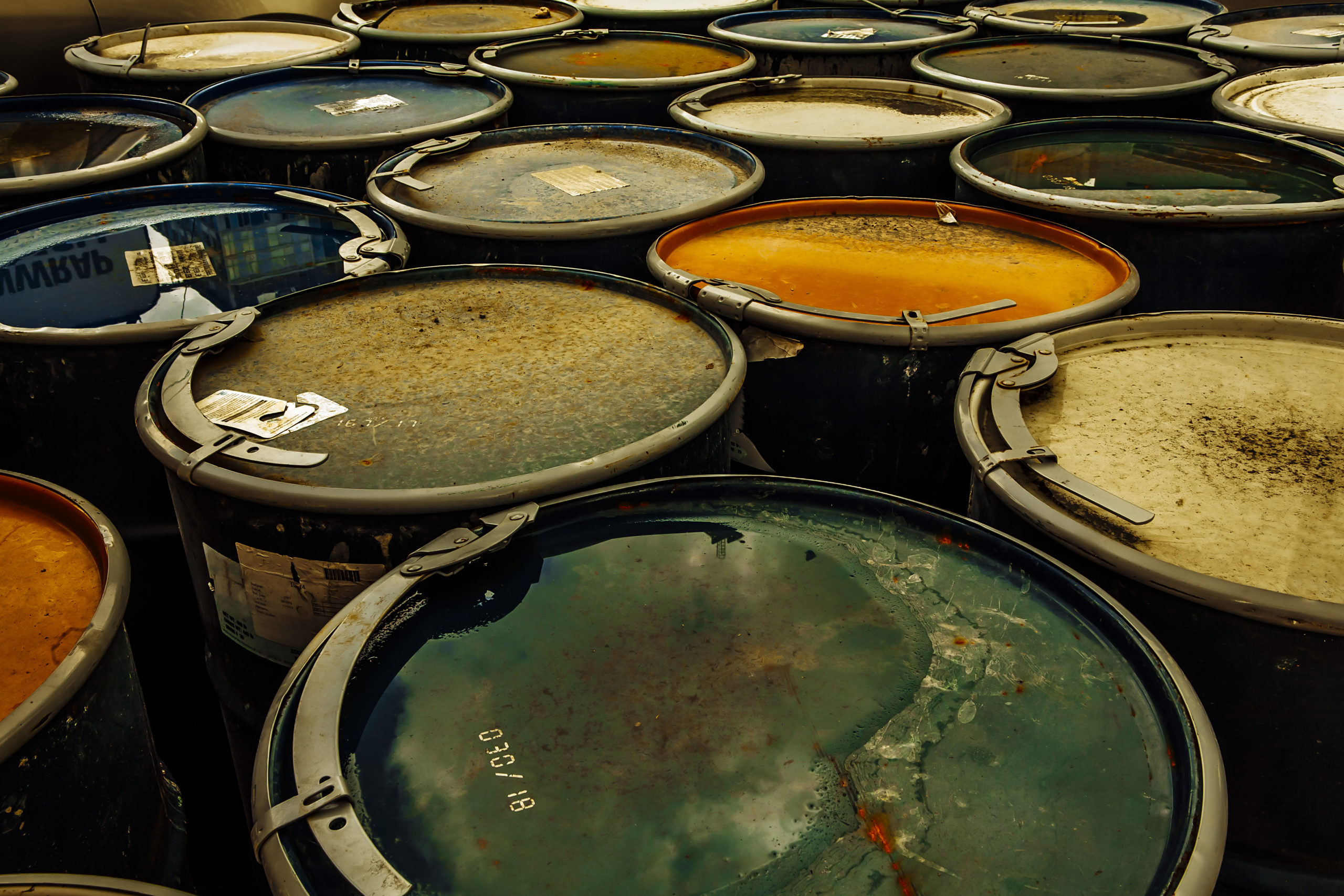
 According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), “Hazardous waste is waste that is dangerous or potentially harmful to our health or the environment. Hazardous wastes can be liquids, solids, gases, or sludges. They can be discarded commercial products, like cleaning fluids or pesticides, or the by-products of manufacturing processes.” There is a growing awareness of the dangerous side effects of hazardous waste contamination. Years ago, many industrial plants discharged heavy metals and unstable organic compounds directly into streams or injected them into the earth’s subsurface through wells, causing illness in populations with close proximity to these toxic sites. This lesson teaches the industrial sources of land, air, and water pollution, the health dangers that environmental pollutants present, and the types of actions that industrial facility workers must complete in order to control industrial pollutants and respond to environmental incidents.
According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), “Hazardous waste is waste that is dangerous or potentially harmful to our health or the environment. Hazardous wastes can be liquids, solids, gases, or sludges. They can be discarded commercial products, like cleaning fluids or pesticides, or the by-products of manufacturing processes.” There is a growing awareness of the dangerous side effects of hazardous waste contamination. Years ago, many industrial plants discharged heavy metals and unstable organic compounds directly into streams or injected them into the earth’s subsurface through wells, causing illness in populations with close proximity to these toxic sites. This lesson teaches the industrial sources of land, air, and water pollution, the health dangers that environmental pollutants present, and the types of actions that industrial facility workers must complete in order to control industrial pollutants and respond to environmental incidents. -
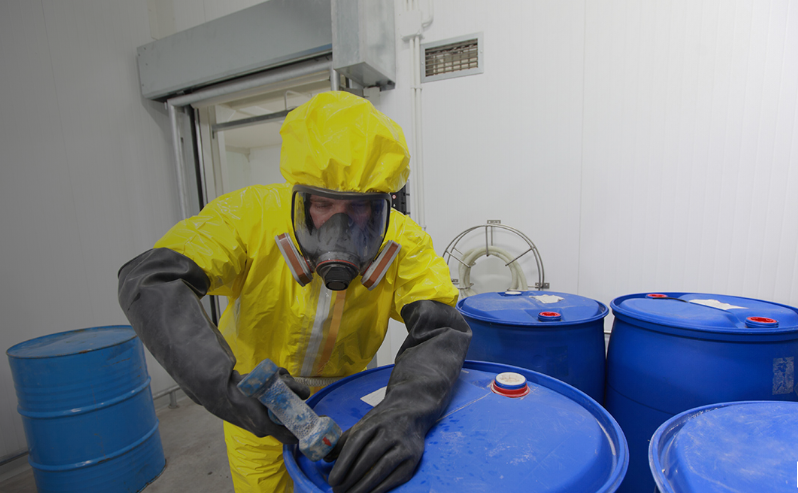

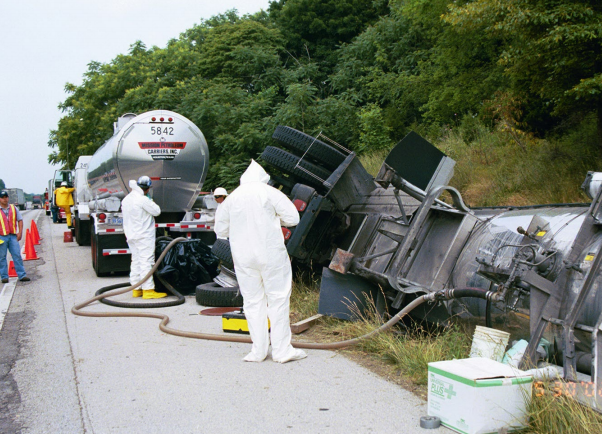
 DOT Packaging Hazardous Materials is part of our DOT Transportation library. It covers the steps for packaging a hazardous material, how to select appropriate hazardous materials packaging and how to determine and prepare required hazardous materials identifiers, including labels, markings, placards, and shipping papers.
DOT Packaging Hazardous Materials is part of our DOT Transportation library. It covers the steps for packaging a hazardous material, how to select appropriate hazardous materials packaging and how to determine and prepare required hazardous materials identifiers, including labels, markings, placards, and shipping papers. -

 When on the road, job, and everywhere in-between, identifying hazardous materials and knowing exactly how to handle them is one of the most important tasks a worker must know. Because of the importance of identifying these hazardous materials properly, the U.S. Department of Transportation (DOT) requires all workers that handle these materials to take safety training in order to help protect themselves as well as others around them.
When on the road, job, and everywhere in-between, identifying hazardous materials and knowing exactly how to handle them is one of the most important tasks a worker must know. Because of the importance of identifying these hazardous materials properly, the U.S. Department of Transportation (DOT) requires all workers that handle these materials to take safety training in order to help protect themselves as well as others around them. -
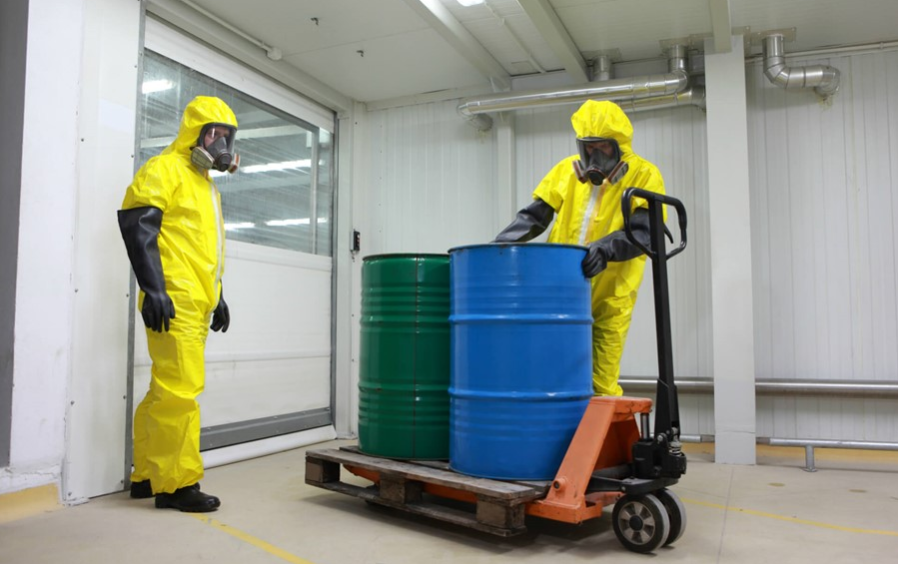

 DOT Hazardous Materials General Awareness consists of five lessons, The goal of this library is to offer the required DOT awareness-level lessons that help save lives in high risk work environments, particularly those that involve transporting hazardous materials. The first lesson is DOT Fundamentals of Hazardous Materials. This lesson provides an overview of the hazardous materials transport process and introduces the learner to the many references used during that process.
DOT Hazardous Materials General Awareness consists of five lessons, The goal of this library is to offer the required DOT awareness-level lessons that help save lives in high risk work environments, particularly those that involve transporting hazardous materials. The first lesson is DOT Fundamentals of Hazardous Materials. This lesson provides an overview of the hazardous materials transport process and introduces the learner to the many references used during that process. -

 Every day in the U.S., 9 people are killed and more than 1,060 people are injured in crashes that are reported to involve a distracted driver. The cause for concern is obvious. Transportation related occupational fatalities are the number one cause of death in the American workforce. The purpose of this lesson is to heighten drivers’ awareness of the dangers of distracted driving and identify ways to stay safe when sharing the road with distracted drivers.
Every day in the U.S., 9 people are killed and more than 1,060 people are injured in crashes that are reported to involve a distracted driver. The cause for concern is obvious. Transportation related occupational fatalities are the number one cause of death in the American workforce. The purpose of this lesson is to heighten drivers’ awareness of the dangers of distracted driving and identify ways to stay safe when sharing the road with distracted drivers. -

 Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is a technique used to slow the process of brain death by restarting the heart and getting a person breathing again. Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) can provide oxygen to the brain and other vital organs of a person who, by every indication, is dead. Used early and correctly, the technique can buy time for the victim until medical attention can be given.
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is a technique used to slow the process of brain death by restarting the heart and getting a person breathing again. Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) can provide oxygen to the brain and other vital organs of a person who, by every indication, is dead. Used early and correctly, the technique can buy time for the victim until medical attention can be given. -

 Many workplaces contain spaces that are considered “confined” because of their configurations. A confined space is large enough and configured in such a way that you can enter and perform assigned work. A confined space has a limited or restricted means of entrance or exit, and a configuration that can make first aid, rescue, evacuation, or other emergency response activities difficult. They are not designed or intended for continuous occupancy. Examples include storage tanks or bins, mixing tanks, railroad tank cars, silos, vaults, and pits. Confined spaces create the ideal conditions for the onset of claustrophobia. Confined spaces can be large or small and above or below ground.
Many workplaces contain spaces that are considered “confined” because of their configurations. A confined space is large enough and configured in such a way that you can enter and perform assigned work. A confined space has a limited or restricted means of entrance or exit, and a configuration that can make first aid, rescue, evacuation, or other emergency response activities difficult. They are not designed or intended for continuous occupancy. Examples include storage tanks or bins, mixing tanks, railroad tank cars, silos, vaults, and pits. Confined spaces create the ideal conditions for the onset of claustrophobia. Confined spaces can be large or small and above or below ground.